In the intricate web of nature, the circle of life unfolds in fascinating ways, with each creature playing a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. Among the myriad interactions that define our ecosystems, the consumption of worms by various animals highlights the interconnectedness of life on Earth. From birds and mammals to reptiles and amphibians, many species rely on worms as a nutritious food source, showcasing the delicate dance of predator and prey. In this blog post, we'll explore the diverse array of animals that feast on worms, shedding light on their feeding habits and the essential role these slimy invertebrates play in the broader ecosystem. Join us as we delve into the wonders of nature's food chain and uncover the surprising relationships that sustain life.
Roundworms Life Cycle In Humans
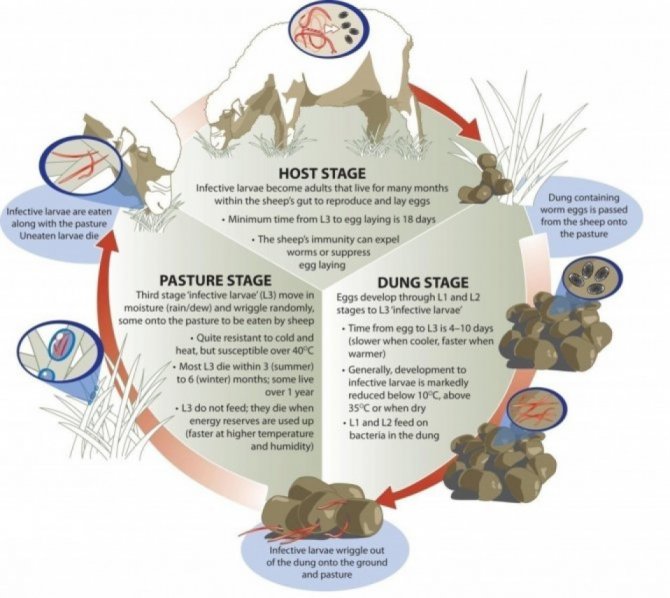
Roundworms, or nematodes, have a fascinating life cycle that can impact human health. These parasites typically enter the human body through contaminated food or water, or by direct contact with infected soil. Once ingested, the larvae migrate to the intestines, where they mature into adult worms. The female roundworm can produce thousands of eggs daily, which are excreted in feces and can contaminate the environment. This cycle continues as new hosts come into contact with the eggs, perpetuating the presence of roundworms in human populations. Understanding this life cycle is crucial for prevention and control, highlighting the intricate connections in the circle of life where animals, humans, and parasites interact.
 animalia-life.club
animalia-life.club What Do Worms Eat?
Worms are fascinating creatures that play a crucial role in the ecosystem, primarily feeding on organic matter. Their diet mainly consists of decomposing leaves, plant material, and microorganisms found in the soil. As they consume this organic matter, worms break it down into nutrient-rich castings, which enrich the soil and promote healthy plant growth. This natural recycling process not only supports their own survival but also benefits countless other organisms in the food chain. By understanding what worms eat, we can appreciate their essential role in the circle of life and the interconnectedness of all living things.
 www.twinkl.co.uk
www.twinkl.co.uk What Animals Eat Worms? 10 Examples With Pictures
In the intricate web of nature, many animals rely on worms as a vital food source, showcasing the interconnectedness of ecosystems. Here are ten examples of creatures that feast on these wriggly invertebrates: 1. **Birds**: From robins to sparrows, many bird species dig into the soil to find worms, which are a rich source of protein.  2. **Moles**: These burrowing mammals are expert hunters of worms, using their keen sense of smell to locate them underground.  3. **Rats**: Often scavengers, rats will consume worms when other food sources are scarce.  4. **Turtles**: Many turtle species enjoy a diet that includes worms, supplementing their primarily herbivorous diets.  5. **Frogs**: These amphibians are known for their insectivorous diets, but they also relish a good worm when they can catch one.  6. **Snakes**: Certain snake species, especially those that are not strictly carnivorous, will eat worms as part of their diet.  7. **Fish**: Many freshwater fish, such as catfish, will eagerly consume worms, making them a popular bait for anglers.  8. **Insects**: Beetles and some ants will feed on worms, particularly when they are in their larval stages.  9. **Bats**: Some bat species, particularly those that are insectivorous, will catch and eat worms as part of their nocturnal diet.  10. **Pigs**: Known for their omnivorous diets, pigs will dig up and eat worms found in the soil while foraging.  Understanding which animals eat worms helps illuminate the circle of life, where each creature plays a role in maintaining ecological balance.
 www.animalquarters.com
www.animalquarters.com Earthworm Life Cycle Identification Cards
In the fascinating web of life, understanding the Earthworm life cycle is crucial for grasping the broader ecological relationships, particularly when exploring what animals eat worms. Earthworm life cycle identification cards serve as a valuable educational tool, illustrating the various stages of development from egg to adult. These cards typically highlight key features such as the size, color, and habitat preferences of earthworms at different life stages, making it easier for enthusiasts and students alike to recognize them in nature. By studying these cards, we can appreciate how earthworms contribute to soil health and nutrient cycling, while also acknowledging their role as a food source for various predators, including birds, amphibians, and small mammals. This interconnectedness emphasizes the importance of each species within the ecosystem, showcasing the intricate circle of life that sustains our planet.
 www.etsy.com
www.etsy.com What Animals Eat Worms?
You Might Also Like: Environmental Manipulation Unseen
In the intricate web of the ecosystem, various animals rely on worms as a vital food source, showcasing the circle of life in action. Birds, particularly robins and sparrows, are well-known for their worm-hunting skills, often seen pecking at the ground in search of these slimy delicacies. Additionally, mammals like moles and hedgehogs dig through the soil to unearth worms, while amphibians such as frogs and toads eagerly snap them up when they emerge. Even some reptiles, including certain species of snakes, will feast on worms as part of their diet. This natural predation not only helps control worm populations but also contributes to nutrient cycling within the soil, highlighting the essential role that worms play in supporting diverse wildlife.
 tagvault.org
tagvault.org